.Net 5/6提供新的创建Windows服务
创建项目选择:
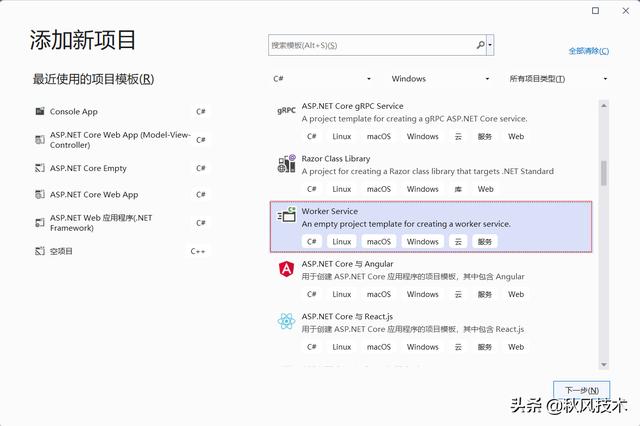
在.Net 5及之后的版本使用新的创建Windows服务
在创建项目后,在nuget安装: Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting.WindowsServices
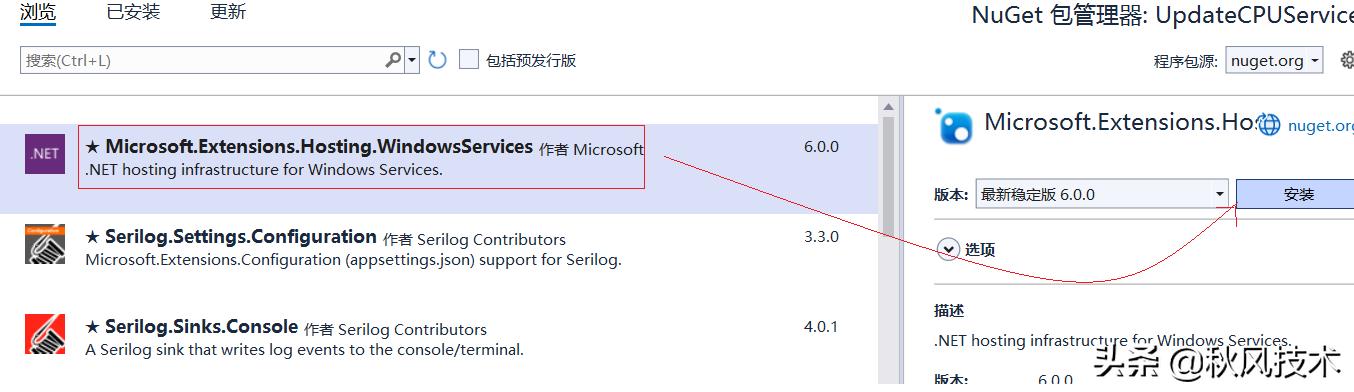
在Nuget种安装Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting.WindowsServices
这里主要是通过服务定时修改cpu的型号信息,是因为我的台式机当时买的是es(当时主要图便宜),在任务管理器中cpu型号是0000的.对于有强迫症的,可以对es的cpu忽略了.
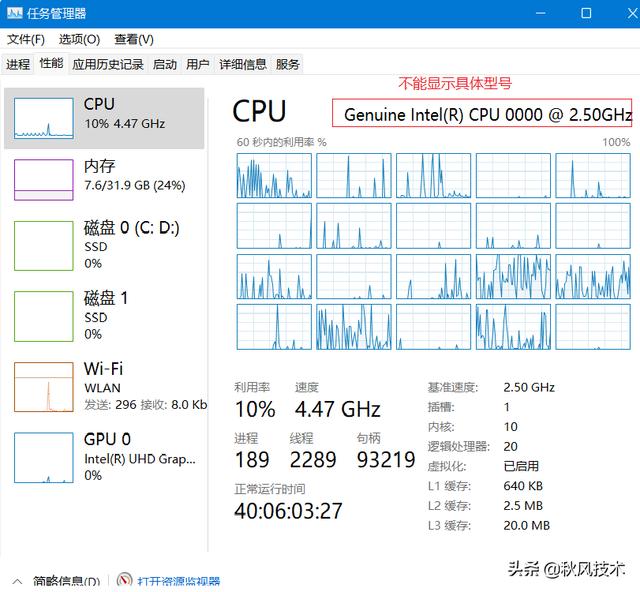
没修改cpu型号信息
服务启动代码:
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using IHost host = Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
//使用在Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting.WindowsServices提供的中间件 UseWindowsService
.UseWindowsService(options =>
{
//指定服务名称
options.ServiceName = "UpdateCPUService";
})
.ConfigureServices(services =>
{
//将UpdateCPUService注入到容器中
services.AddHostedService<UpdateCPUService.UpdateCPUService>();
})
.Build();
await host.RunAsync();
具体服务代码:
using System.Runtime.Versioning;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using Microsoft.Win32;
namespace UpdateCPUService
{
public class UpdateCPUService : BackgroundService
{
private readonly ILogger<UpdateCPUService> _logger;
public UpdateCPUService(ILogger<UpdateCPUService> logger)
{
this._logger = logger;
}
//只支持Windows
[SupportedOSPlatform("windows")]
protected override async Task ExecuteAsync(CancellationToken stoppingToken)
{
//while (!stoppingToken.IsCancellationRequested)
//{
// _logger.LogInformation("Worker running at: {time}", DateTimeOffset.Now);
// await Task.Delay(1000, stoppingToken);
//}
while (!stoppingToken.IsCancellationRequested)
{
_logger.LogInformation("Worker running at: {time}", DateTimeOffset.Now);
try
{
//注册表路径:计算机\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\HARDWARE\DESCRIPTION\System\CentralProcessor
RegistryKey root = Registry.LocalMachine;
RegistryKey? hardware = root.OpenSubKey("HARDWARE", true);
if (hardware != null)
{
var description = hardware!.OpenSubKey("DESCRIPTION", true);
var system = description!.OpenSubKey("System", true);
//获取CentralProcessor节点
var centralProcessor = system!.OpenSubKey("CentralProcessor", true);
//子节点对应cpu核心数(包含超线程)
for (int i = 0; i < centralProcessor!.SubKeyCount; i++)
{
RegistryKey? cpuNode = centralProcessor.OpenSubKey($"{i}", true);
//修改cpu型号信息,这里不考虑灵活性,写死,可以加配置文件
cpuNode!.SetValue("ProcessorNameString", "Intel(R) Core(TM) i9-10900 CPU @ 2.50GHz");
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError("Worker running at: {message}", ex.Message);
}
//测试为1分钟,正式为30分钟
await Task.Delay(TimeSpan.FromMinutes(1), stoppingToken);
}
}
}
}
创建Windows服务相关命令:
#通过sc create创建Windows服务 sc.exe create "UpdateCPUService" binpath="D:/codes/csharp/UpdateCPUService/bin/Release/net6.0/UpdateCPUService.exe" #通过sc delete 删除Windows服务 sc.ese delete "UpdateCPUService" #启动服务 net start updatecpuservice #停止服务 net stop updatecpuservice
服务运行后:
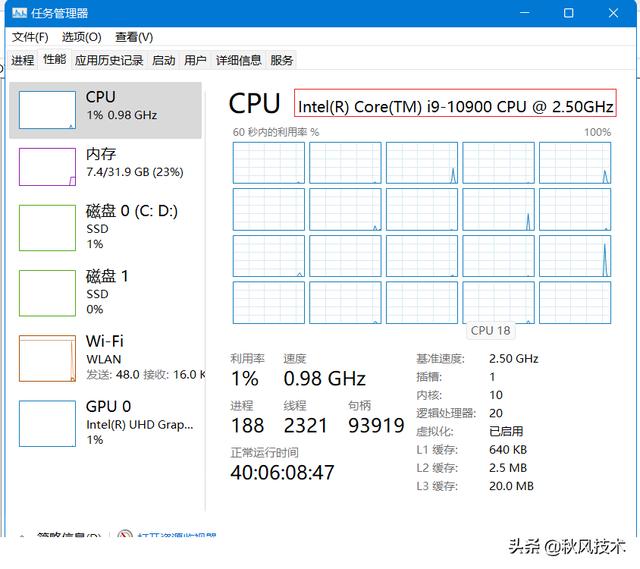
Windows服务修改cpu型号信息
注意: 因为操作注册表程序要有权限. .Net程序要提高权限的话,可以添加 应用程序清单文件(app.maniftest)
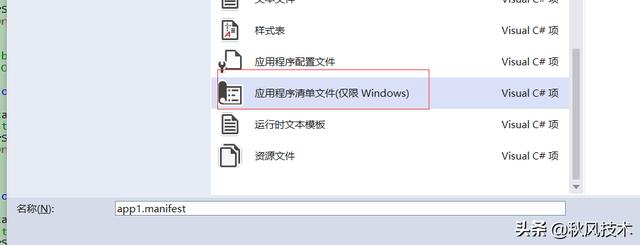
在.Net程序中添加应用程序清单文件,将程序提升权限为管理员权限
<!--使用管理员权限--> <requestedExecutionLevel level="requireAdministrator" uiAccess="false" />
新的实现方式是新瓶装老酒
先看看UseWindowsService源码:
public static IHostBuilder UseWindowsService(this IHostBuilder hostBuilder)
{
return UseWindowsService(hostBuilder, _ => { });
}
public static IHostBuilder UseWindowsService(this IHostBuilder hostBuilder, Action<WindowsServiceLifetimeOptions> configure)
{
if (WindowsServiceHelpers.IsWindowsService())
{
// Host.CreateDefaultBuilder uses CurrentDirectory for VS scenarios, but CurrentDirectory for services is c:\Windows\System32.
hostBuilder.UseContentRoot(AppContext.BaseDirectory);
hostBuilder.ConfigureLogging((hostingContext, logging) =>
{
Debug.Assert(RuntimeInformation.IsOSPlatform(OSPlatform.Windows));
logging.AddEventLog();
})
.ConfigureServices((hostContext, services) =>
{
Debug.Assert(RuntimeInformation.IsOSPlatform(OSPlatform.Windows));
services.AddSingleton<IHostLifetime, WindowsServiceLifetime>(); //将WindowsServiceLifetime添加到容器中
services.Configure<EventLogSettings>(settings =>
{
Debug.Assert(RuntimeInformation.IsOSPlatform(OSPlatform.Windows));
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(settings.SourceName))
{
settings.SourceName = hostContext.HostingEnvironment.ApplicationName;
}
});
services.Configure(configure);
});
}
return hostBuilder;
}
中间件源码:
using System;
using System.Runtime.Versioning;
using System.ServiceProcess;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Options;
namespace Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting.WindowsServices
{
//WindowsServiceLifetime实现ServiceBase
//可以看到还是基于ServiceBase的封装
[SupportedOSPlatform("windows")]
public class WindowsServiceLifetime : ServiceBase, IHostLifetime
{
private readonly TaskCompletionSource<object> _delayStart = new TaskCompletionSource<object>(TaskCreationOptions.RunContinuationsAsynchronously);
private readonly ManualResetEventSlim _delayStop = new ManualResetEventSlim();
private readonly HostOptions _hostOptions;
public WindowsServiceLifetime(IHostEnvironment environment, IHostApplicationLifetime applicationLifetime, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory, IOptions<HostOptions> optionsAccessor)
: this(environment, applicationLifetime, loggerFactory, optionsAccessor, Options.Options.Create(new WindowsServiceLifetimeOptions()))
{
}
public WindowsServiceLifetime(IHostEnvironment environment, IHostApplicationLifetime applicationLifetime, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory, IOptions<HostOptions> optionsAccessor, IOptions<WindowsServiceLifetimeOptions> windowsServiceOptionsAccessor)
{
Environment = environment ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(environment));
ApplicationLifetime = applicationLifetime ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(applicationLifetime));
Logger = loggerFactory.CreateLogger("Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime");
if (optionsAccessor == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(optionsAccessor));
}
if (windowsServiceOptionsAccessor == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(windowsServiceOptionsAccessor));
}
_hostOptions = optionsAccessor.Value;
ServiceName = windowsServiceOptionsAccessor.Value.ServiceName;
CanShutdown = true;
}
private IHostApplicationLifetime ApplicationLifetime { get; }
private IHostEnvironment Environment { get; }
private ILogger Logger { get; }
public Task WaitForStartAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
cancellationToken.Register(() => _delayStart.TrySetCanceled());
ApplicationLifetime.ApplicationStarted.Register(() =>
{
Logger.LogInformation("Application started. Hosting environment: {envName}; Content root path: {contentRoot}",
Environment.EnvironmentName, Environment.ContentRootPath);
});
ApplicationLifetime.ApplicationStopping.Register(() =>
{
Logger.LogInformation("Application is shutting down...");
});
ApplicationLifetime.ApplicationStopped.Register(() =>
{
_delayStop.Set();
});
Thread thread = new Thread(Run); //创建一个后台线程
thread.IsBackground = true;
thread.Start(); // Otherwise this would block and prevent IHost.StartAsync from finishing.
return _delayStart.Task;
}
private void Run()
{
try
{
Run(this); // This blocks until the service is stopped.
_delayStart.TrySetException(new InvalidOperationException("Stopped without starting"));
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_delayStart.TrySetException(ex);
}
}
public Task StopAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
// Avoid deadlock where host waits for StopAsync before firing ApplicationStopped,
// and Stop waits for ApplicationStopped.
Task.Run(Stop, CancellationToken.None);
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
// Called by base.Run when the service is ready to start.
protected override void OnStart(string[] args)
{
_delayStart.TrySetResult(null);
base.OnStart(args);
}
// Called by base.Stop. This may be called multiple times by service Stop, ApplicationStopping, and StopAsync.
// That's OK because StopApplication uses a CancellationTokenSource and prevents any recursion.
protected override void OnStop()
{
ApplicationLifetime.StopApplication();
// Wait for the host to shutdown before marking service as stopped.
_delayStop.Wait(_hostOptions.ShutdownTimeout);
base.OnStop();
}
protected override void OnShutdown()
{
ApplicationLifetime.StopApplication();
// Wait for the host to shutdown before marking service as stopped.
_delayStop.Wait(_hostOptions.ShutdownTimeout);
base.OnShutdown();
}
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (disposing)
{
_delayStop.Set();
}
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
}
}
总结
- 老的方式,单一继承ServiceBase,通用性特好,支持.Net Framework/.Net Core及.Net 5/6/7,简单的Windows服务直接使用.
- 新的中间件方式,只能在.Net 5及更高的版本使用,在复杂的Windows服务要好一些.可以使用容器,进行依赖注入