1. 前言
本文主要讲解Linux怎么创建大于2T空间的分区,因为fdisk只支持mbr分区,而大容量的分区需要使用GPT。MBR分区表最多只能识别2TB左右的空间,大于2TB的容量将无法识别从而导致硬盘空间浪费;GPT分区表则能够识别2TB以上的硬盘空间。

2. 创建GPT分区
假设目前一块sdb磁盘,有10G的空闲空间,操作如下:
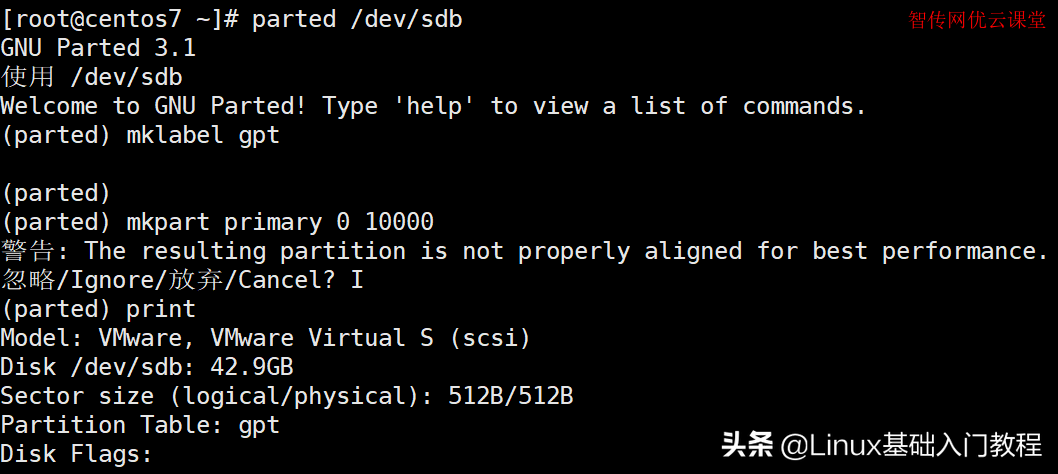
[root@zcwyou ~]# parted /dev/sdb
GNU Parted 3.1
使用 /dev/sdb
Welcome to GNU Parted! Type 'help' to view a list of commands.
创建gpt标签
(parted) mklabel gpt
创建10000M的分区,即10G
(parted) mkpart primary 0 10000
警告: The resulting partition is not properly aligned for best performance.
忽略/Ignore/放弃/Cancel? I
查看分区表
(parted) print
Model: VMware, VMware Virtual S (scsi)
Disk /dev/sdb: 42.9GB
Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B
Partition Table: gpt
Disk Flags:
创建GPT分区
3. 重读分区表
partprobe命令用于重读分区表,当出现删除文件后,出现仍然占用空间。可以partprobe在不重启的情况下重读分区。
[root@zcwyou ~]# partprobe
4. 格式化GPT分区
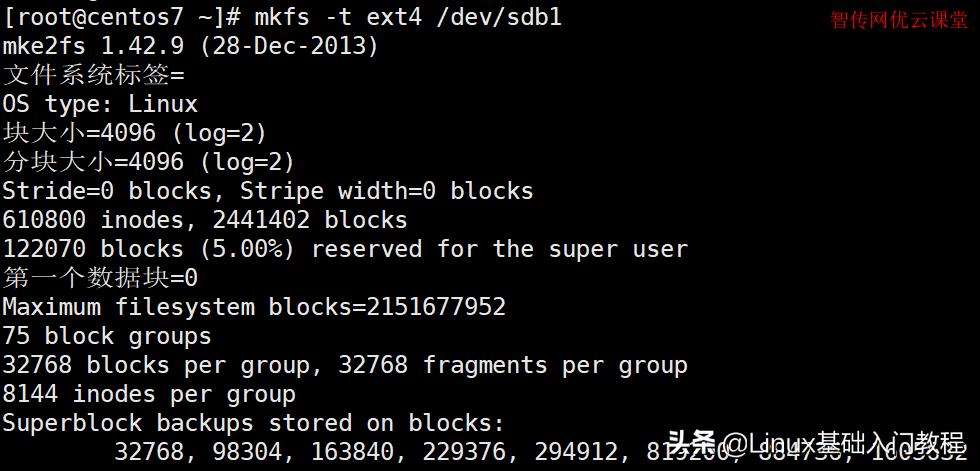
[root@zcwyou ~]# mkfs -t ext4 /dev/sdb1
mke2fs 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013)
文件系统标签=
OS type: Linux
块大小=4096 (log=2)
分块大小=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
610800 inodes, 2441402 blocks
122070 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
第一个数据块=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=2151677952
75 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8144 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632
Allocating group tables: 完成
正在写入inode表: 完成
Creating journal (32768 blocks): 完成
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: 完成
格式化GPT分区
5. 查看分区信息
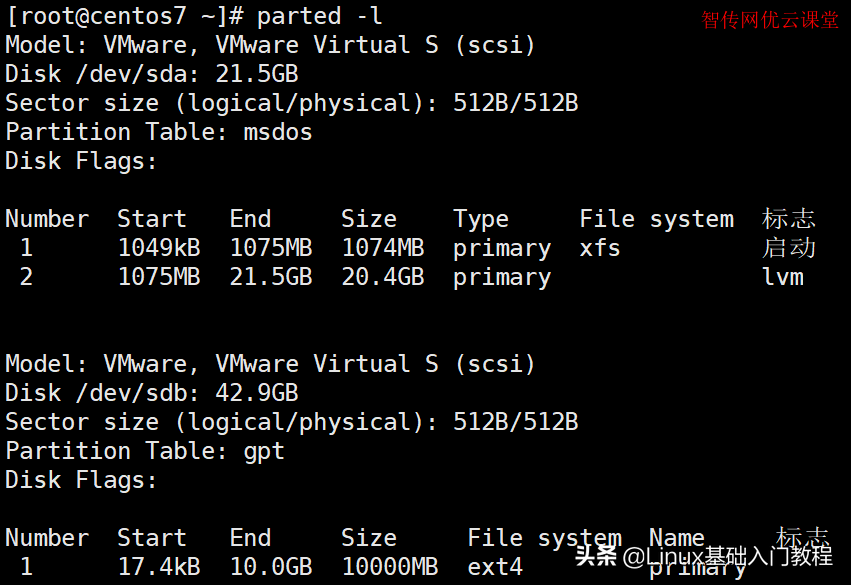
[root@zcwyou ~]# parted -l
Model: VMware, VMware Virtual S (scsi)
Disk /dev/sda: 21.5GB
Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B
Partition Table: msdos
Disk Flags:
Number Start End Size Type File system 标志
1 1049kB 1075MB 1074MB primary xfs 启动
2 1075MB 21.5GB 20.4GB primary lvm
Model: VMware, VMware Virtual S (scsi)
Disk /dev/sdb: 42.9GB
Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B
Partition Table: gpt
Disk Flags:
Number Start End Size File system Name 标志
1 17.4kB 10.0GB 10000MB ext4 primary
使用parted命令查看GPT分区
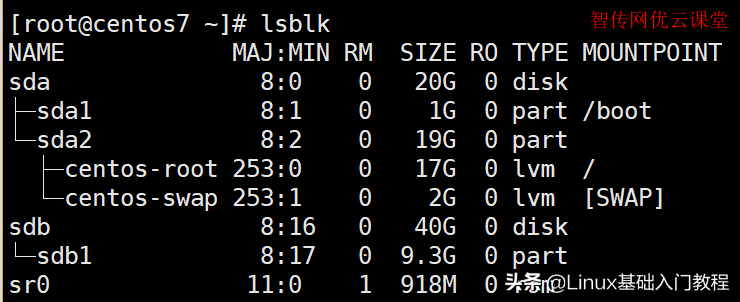
[root@zcwyou ~]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 20G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
└─sda2 8:2 0 19G 0 part
├─centos-root 253:0 0 17G 0 lvm /
└─centos-swap 253:1 0 2G 0 lvm [SWAP]
sdb 8:16 0 40G 0 disk
└─sdb1 8:17 0 9.3G 0 part
sr0 11:0 1 918M 0 rom
使用lsblk命令查看GPT分区
6. 挂载文件系统
[root@centos7 ~]# mkdir /mnt/sdb1 [root@centos7 ~]# mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/sdb1
7. 查看挂载文件系统
bash [root@centos7 ~]# df -TH ¨G6G bash [root@zcwyou ~]# vi /etc/fstab
最后一行如下:
/dev/sdb1 /mnt/sdb1 ext4 defaults 0 0
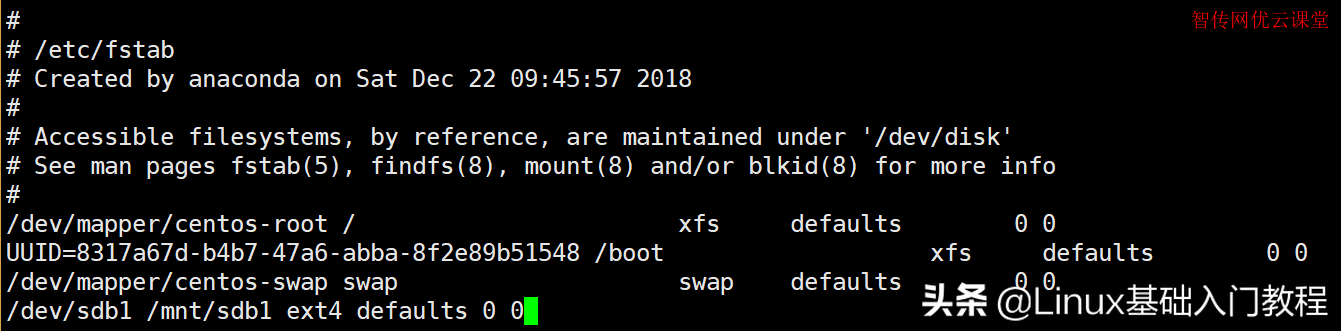
实现开机自动挂载文件系统
9. 总结
GPT分配64bits给逻辑块地址,因而使得最大分区大小在264-1个扇区成为可能。对于每个扇区大小为512字节的磁盘,那意味着可以有9.4ZB(9.4×1021字节)或8 ZiB个512字节(9,444,732,965,739,290,426,880字节或18,446,744,073,709,551,615(264-1)个扇区×512(29)字节每扇区)。所以大容量分区只能使用GPT。
本文已同步至博客站,尊重原创,转载时请在正文中附带以下链接:
https://www.linuxrumen.com/rmxx/790.html